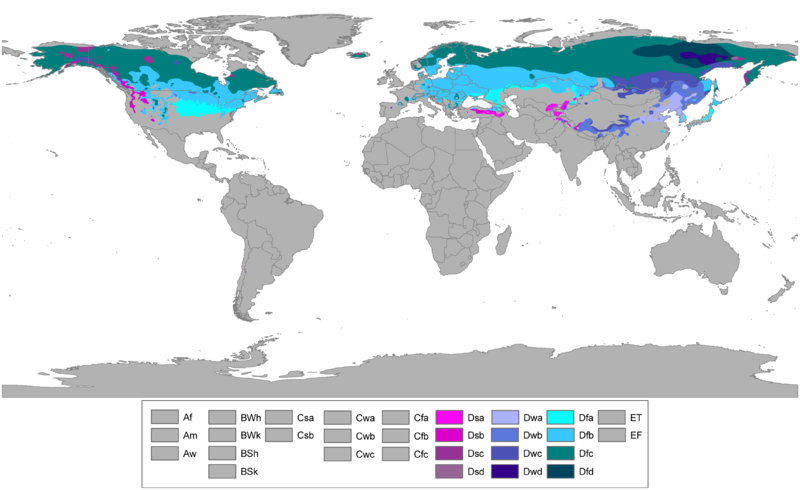
Continental Climate
Key Points
1) Is not located near a large body of water (lake, ocean).
2) SInce it is not by a large body of water, the temperature range is much more drastic.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Continental_climate
2) SInce it is not by a large body of water, the temperature range is much more drastic.
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Continental_climate
Summary
Continental climate is generally located in the interior of Canada, where regions are not near a very large lake, or ocean. BEcause there is no ocean to moderate the climate and temperature, the winter and summer months have a much more drastic temperature range. There is less rain on a daily basis as well.