Simon Fraser
Key Points

- Became a partner in the NWC in 1801
- Built Fort Mcleod, Fort St. James, Fort Fraser and Fort George (Prince George)
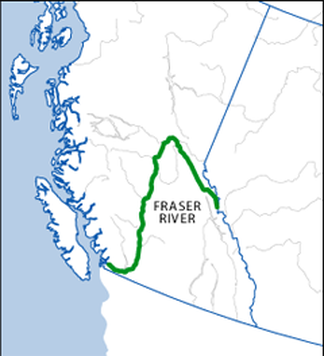
- Was the first to sail the Fraser river through the Fraser Canyon
- Established the canyon as Hells Gate
- David Thompson named the Fraser river in honour of Simon Fraser
- Simon Fraser named the Thompson River in honour of David Thompson
- Built Fort Mcleod, Fort St. James, Fort Fraser and Fort George (Prince George)
- Was the first to sail the Fraser river through the Fraser Canyon
- Established the canyon as Hells Gate
- David Thompson named the Fraser river in honour of Simon Fraser
- Simon Fraser named the Thompson River in honour of David Thompson
Summary

Simon Fraser (1776–18 August 1862) was a fur trader and explorer who charted most of British Columbia. Fraser worked for the North West Company in 1805 he was put in charge of the company's operations west of the Rocky Mountains. He built trading posts in Fort St. James, Fort Fraser, and Fort George (Prince George). In 1808 he explored the Fraser River, whcih was named in Honour of him by David Thompson. Fraser was put through the obstacles of the Fraser Canyons, which he named Hells Gate due to it's extremities. Simon Fraser afterwards name the Thompson river after his fellow Nor'wester David Thompson.